| Preface
Requirements management is an
engineering problem that everyone is concerned about,
and it seems to be untechnical, but it is difficult
to solve. This paper proposes a model-based requirements
management method, and based on this theory, the mainstream
modeling tool EA is selected, and the corresponding
requirements management tool is customized. It is
hoped that peers who are facing the same requirements
management challenges will be inspired.
Body
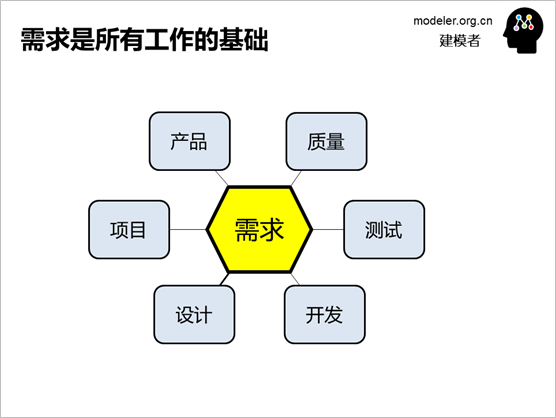
Requirements are the basis of
a lot of work:
The scope management and
workload estimation of the project should be based
on requirements
A sufficient analysis of requirements,
such as functionality, extensions, and performance,
is required to effectively design the framework
and operation process of the software.
Testing also requires the
design of test cases based on requirements and the
development of verification standards.
A lot of the work of a product
manager is based on requirements, such as product
requirements analysis, product design, and product
release management.
Demand management is also the
most problematic link in the software development
process and system engineering, whether it is a control
system on aviation, aerospace and automobiles with
high reliability requirements, or a business system
for enterprise informatization, the quality of requirements
has always been paid attention to, but has never been
effectively solved.

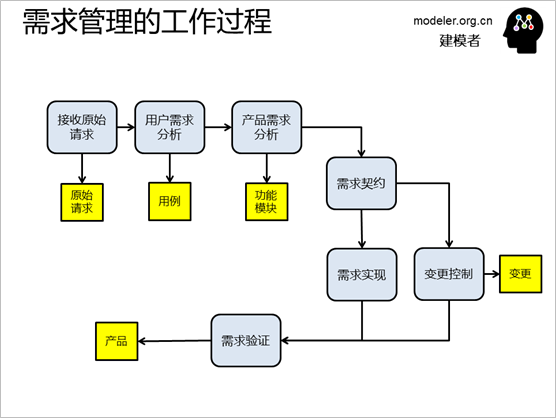
The working process of requirements
is generally as follows:
First, the original request
of the user is received, and then the demand personnel
analyze the user's requirements and describe the
use case clearly.
On the basis of clear user
needs, further product demand analysis is carried
out to define the functional modules of the system;
The developer and the user
sign a demand contract to clarify what to develop,
how much work to invest, estimate the cost and time,
and determine the budget.
The development team then
develops based on the requirements, and in the process,
the user's requirements are subject to change control
so that the quality product can be delivered on
the expected time.
When the development is completed,
it is verified based on the requirements, and only
those that are qualified can become the products
delivered to users.
Although the development process
can be carried out iteratively, from the user's point
of view, a high-level development team should confirm
the requirements before development, and the delivered
product should also meet the quality requirements.
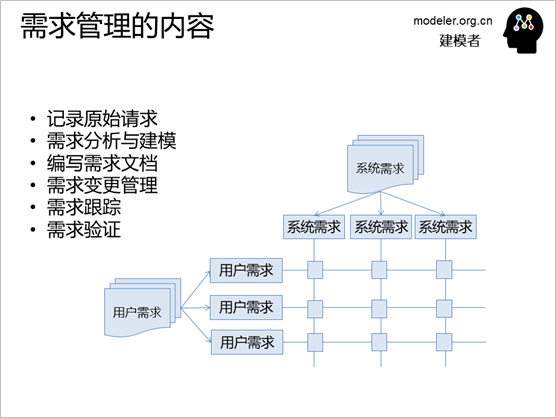
Based on the above requirements
workflow, the following requirements management content
can be sorted out:
The user's original request
Models for requirements analysis,
e.g., use case models, interface models, and models
that describe non-functional requirements.
The system or software itself
that is being developed or delivered.
Use cases for requirements
validation.
Defects or inconsistencies
in requirements found
The management content of requirements
seems to be varied, and it should be related to the
subsequent design, development, and testing of the
artifacts, so that there are more related contents,
how to manage them well? The management content of
various jobs can be organized into three categories:
Documents, such as requirements
documents, design documents, development documents,
and test documents.
Item data, e.g. a list of
required use cases, a list of designed modules,
a directory of developed codes, and a list of tested
bugs.
Models, such as requirements
models, architecture models, data models, code models,
and test models.
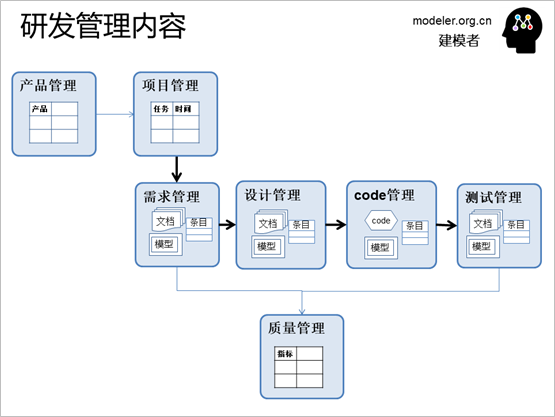
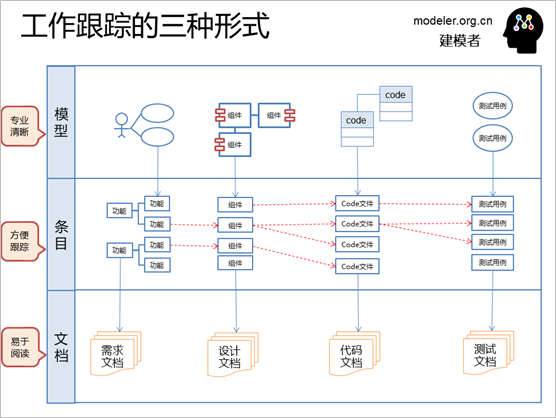
Although each content is different,
the same form of management method is basically the
same. Among the three forms, the model is suitable
as a form of specialized analysis and design work;
Documentation can be read by everyone, especially
those who are not designers and developers; Item data
is suitable for tracking management.
Through the above analysis, there
is no doubt that the model is the key to the whole
research and development process, if there is no adequate
analysis and design, the quality of the management
content is not good, the organization is not clear,
and the best management process and tools are not
well managed. It is for this reason that we propose
a model-based approach to requirements management,
and the main ideas are:
Professional requirements
analysis, system design, software design and test
analysis design based on the model.
Based on the hierarchical
relationship in the logical relationship of the
model, the model is turned into a list of items
for tracking management, and the focus is to establish
the association between various model elements,
such as: the implementation relationship between
the use cases in the requirements and the components
in the design, and the tracking relationship between
the bugs in the test and the corresponding requirements
use cases or components.
Various documents can be generated
based on the model, so that the documents are naturally
associated with the model, and can also be managed
in the form of a list. By converting the model into
list data, it is easy to support the forms of object
lists, impact analysis matrices, tracking trees,
kanbans, statistical charts, etc., and the requirement
difference analysis of each version is also much
more convenient.
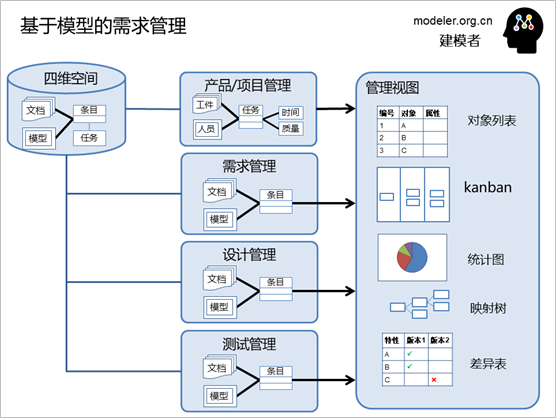
To this end, we have specially
developed a model-based requirements management tool
iSpace, which is based on the model generation of
the mainstream modeling tool EA for management of
itemized data, and can be extended to the models of
other modeling tools according to the needs of users
in the future.
The following are screenshots and descriptions of
some usage scenarios of iSpace.
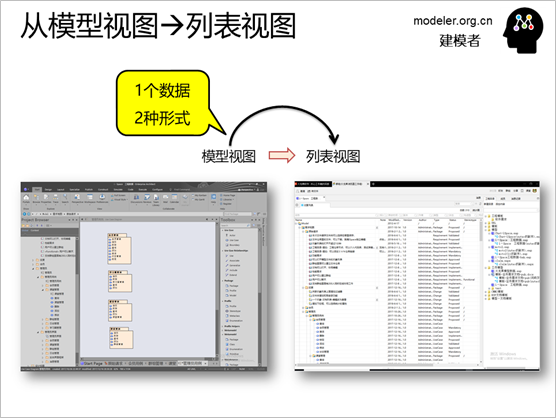
The elements in the EA model
can be easily tracked and managed by using the list
view of iSapce.
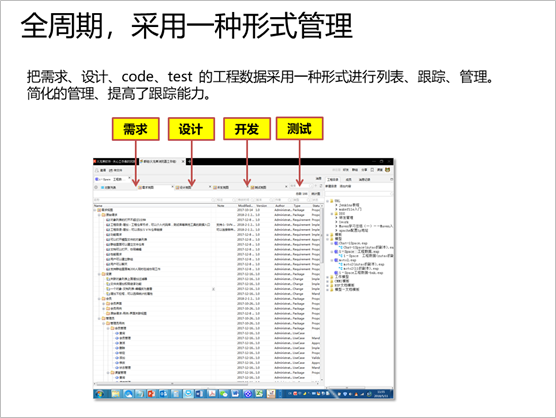
Based on the full-cycle model
of systems engineering or software engineering: requirements
model, design model, code model, and test model, all
of which can be browsed and managed in the view of
the item list. This makes it easy to manage completely,
and all kinds of management (requirements management,
design management, code management, test management)
have a set of methods, some of which overlap, and
if they are managed separately in different tools,
the correlation between them is a complex work. If
all the models are built in one modeling tool, and
then correspond to various management views based
on the models, the seemingly complex management will
be simple together, and many association problems
will be easily solved.
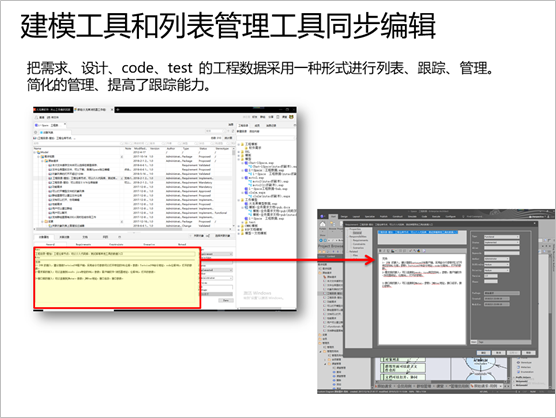
As follows, if you edit the corresponding
elements and attributes in iSpace, they will be automatically
synchronized to the modeling tool and vice versa.
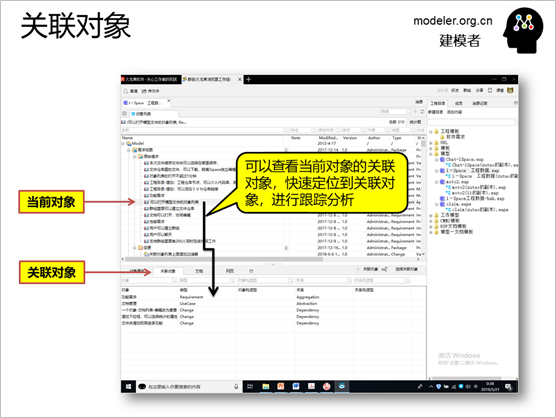
It is also very convenient to
select an element, and quickly select other associated
elements through the association selector, which is
much more convenient to operate, and the key is that
the relationship between the corresponding elements
on the model diagram can also be automatically synchronized
in the modeling tool EA.
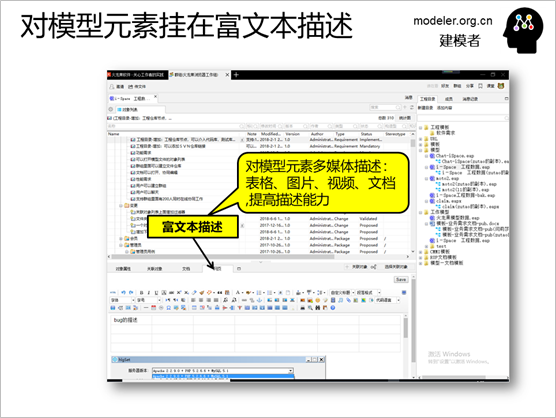
In order to compensate for the
problem of a relatively simple description of the
modeling tool (mainly text-based), a rich text editing
area is provided where users can:
Create a table
Paste the image
Upload the video
Hook up documents
This is useful for some work
scenarios, such as:
The demand person should put
an interface prototype diagram or a professional
algorithm diagram under a use case.
The tester finds a bug, takes
a screenshot, and puts the screenshot under a bug
model element.
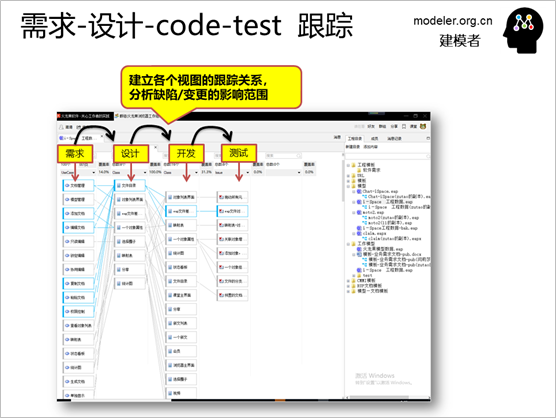
Based on the relationship between
the elements in the model, you can quickly generate
an association context diagram, which is of great
value for the impact analysis of requirements changes
or bugs.
The following is a screenshot
of the working scenarios for various management requirements.

The following is the change impact
analysis, after establishing various models (requirement
model, design model, code model, test model), if the
user proposes a requirement change, you can generate
an association context diagram, select a change, and
you can view the content of all models affected.

The following is the bug impact
analysis, after establishing various models (requirement
model, design model, code model, test model), if a
bug is found, you can generate an association context
diagram, select a bug, and you can view the content
of all models affected.

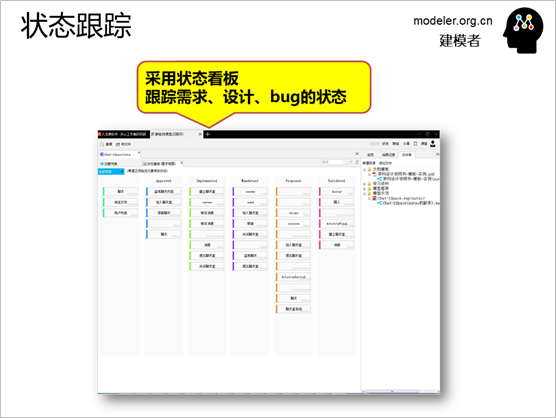
Requirements also need to track
various states (proposed, to be developed, to be tested,
to be released, published), at present, Kanban is
a very practical tracking method, iSpace can automatically
assign to the status column of Kanban according to
the status of various elements, and can also change
the state of elements by dragging. If it is equipped
with a large screen, it is a good electronic signage.
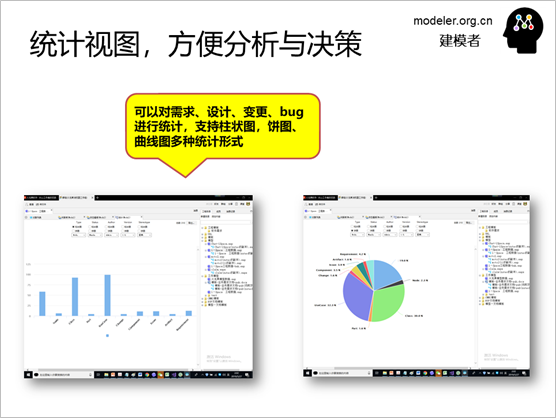
Requirement management needs to
carry out a variety of statistics, such as demand
completion statistics, requirements verification coverage
statistics, demand quality statistics, for which a
variety of statistical charts are provided, statistical
data are from the model, users can convert to the
statistical view at any time, real-time understanding
of various information of requirements, and guide
related development, testing and management work.
postscript
I hope you have benefited from
reading this.
If you are willing to share your
experience, please submit it to us.
If you are interested in our
training, consulting and tools:
Modeling Too£∫EA
Model-based requirements management
tool£∫iSpace
Course£∫MBSE
(Model-Based Systems Engineering)
Course£∫Model-Based Requirements
Analysis, Modeling and Management
Consulting Solution£∫MBSE
(Model-Based Systems Engineering)
Consulting Solution£∫Model-Driven
Development Based on UML
All modeling-related courses£∫http://www.modeler.org.cn/course/index.asp
All Requirements Management
Courses£∫http://course.uml.org.cn/course/requirement.asp
Consulting Solution£∫Model-Based
Engineering Management
Welcome to contact us: Zutao@uml.net.cn
|
