|
Preface
At present, it is the era of
knowledge explosion, people have accumulated a lot
of knowledge, with the rapid development of science
and technology, explosive knowledge and technology,
people are overwhelmed and exhausted. Despite the
constant efforts to control the chaos caused by the
development of various processes and the division
of disciplines, the way knowledge itself is described
has always been the key to simplifying the problem:
- The concise and coherent
mathematical formula of mathematics is far better
than the ninety-nine mantra of the abacus,
- With physical formulas, we
can understand the universal laws of the material
world simply and clearly.
In addition to physics and mathematics,
which are scientific reasoning formulas, and human
natural language, we also need a form that can describe
various concepts, and organize them clearly, so that
we can understand the relationship between various
concepts at a glance. Because of the unique human-oriented
logical thinking of software logic and the characteristics
of work involving various industries, the domain modeling
that starts with the UML class diagram of the software
industry modeling specification can be used as a method
for us to organize knowledge in various fields.

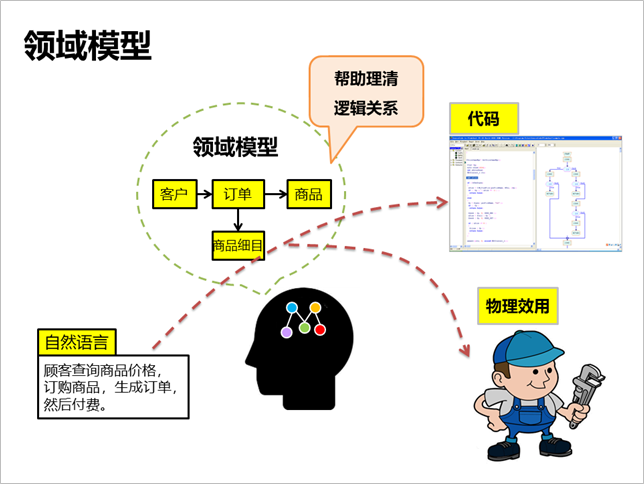
The output of domain modeling
is the domain model, which is a form that describes
natural language more clearly than natural language,
organizes various concepts graphically, helps people
understand complex information, and is the basis for
effective analysis before specific work.
This article is the knowledge
model of physics in the second semester of the second
semester of junior high school that I helped my daughter
CC organize with domain modeling methods£∫
- Let the reader know that
domain modeling can help collate a variety of expertise
and be useful for everyone, from students and engineers
to scientists.
- Other parents and teachers
who are concerned about secondary school students
are also welcome as references.
Body
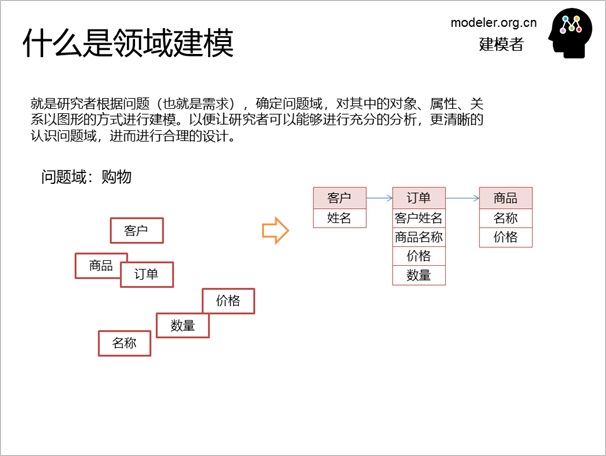
First, let's look at what domain
modeling is. It is important to learn a method and
understand the basic concepts, and there are 2 core
concepts here:

Now that we understand the basic
concepts, let's take a look at what domain modeling
is:
In the software industry, domain
modeling is a very effective method because of the
need to understand business domain knowledge, and
it is basically a consensus that domain modeling is
a necessary skill for product managers, requirements
analysts, architects, and software development engineers.
In other fields, such as systems engineering, hardware,
various professional fields (such as optoelectronics,
mechanics, electronics, communications) or more broadly,
secondary schools and universities, domain modeling
is basically a state that most people do not understand
at all, and even if they occasionally involve software
projects, they will think that it is a seemingly useful
but uncertain method and turn away. Here, with my
20 years of experience in dozens of projects involving
more than 10 fields, domain modeling is really a very
important basic skill, as long as you want to sort
out the huge amount of knowledge, whether it is related
to software or not, you can use it, it can help you
clarify the knowledge context, concisely grasp the
essence of the problem.
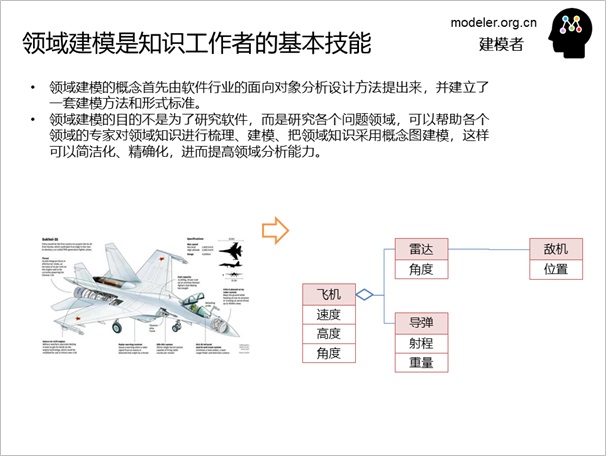
Domain modeling is mainly to organize
various knowledge and concepts in the problem domain,
which is much like people using natural language to
describe various things in the real world with various
words, and these words themselves are the classification
of things, such as the noun "table, plane, elephant".
However, because of the universality of writing, natural
language can only be described in the form of line
by line, word by word, and then the person who reads
it, according to his own knowledge map, organizes
various concepts into various conceptual relationships
in his mind, but the concepts in each person's mind
do not have a clear presentation form, resulting in
confusion in various conceptual relationships. The
domain model is to use UML class diagrams to model
various concepts in the domain, so that the logical
relationships in the mind have a clear form, which
is much better.
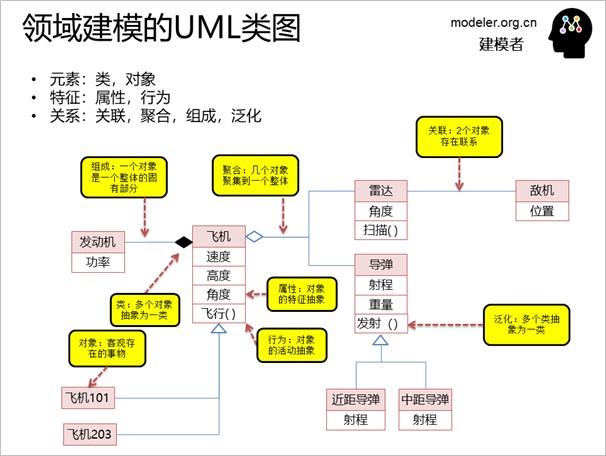
Let's take a look at the elements,
characteristics, and relationships of a class diagram
for domain modeling:
Challenges of domain modeling
There are 3 key aspects of domain
modeling:
1.Have a deep understanding of
object-oriented analysis methods and be able to identify
objects, classes, and relationships from requirements
descriptions.
2.Accurately understand the modeling
mechanism of classes, attributes, behaviors, and relationships
in UML class diagrams.
3. Be familiar with the problem
area and be able to grasp the core knowledge of the
problem area.
These three elements are undoubtedly
mutually reinforcing, and must be organically combined
to achieve complete domain modeling. Most of what
you see in books is the domain modeling of e-commerce
and information management systems, which focuses
on data and has an innate close correlation with computer
data processing, so domain modeling is not complicated
and easy to reach a consensus. For those logical domains
with complex logic and inconspicuous data relationships,
domain modeling has a higher challenge.
Lower grade 8, domain modeling
of physics subject knowledge
In order to illustrate that domain
modeling is a basic ability, here is a summary of
domain modeling in physics under the eighth grade
compiled for my daughter CC£∫
- I want everyone to understand
how important modeling is for knowledge understanding.
- Parents of other secondary
school students are also welcome to use as references.
- There will be domain modeling
in other disciplines in the future: )
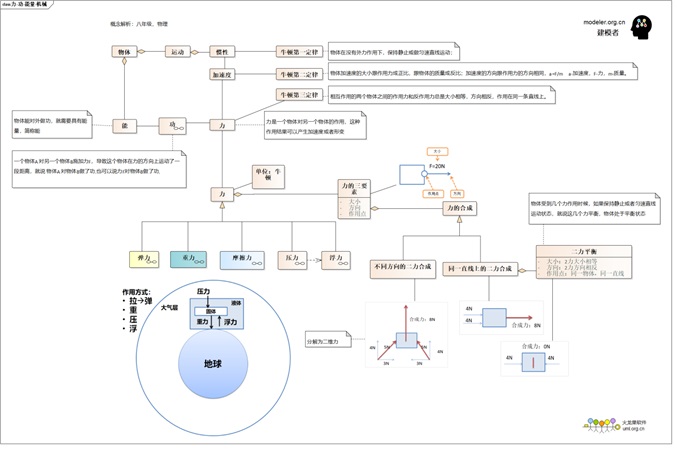
General framework of forces:
First of all, it should be made
clear that the principles of mechanical motion are
taught in the second year of junior high school physics,
which involves some basic basic principles:
- The object has inertia£∫the
object remains stationary or moves in a straight
line at a uniform speed without the action of external
force; (This is Newton's first law)
- To change the inertia
of an object, a force needs to be applied£∫the
acceleration of an object is proportional to the
force and inversely proportional to the mass of
the object; The direction of acceleration is the
same as the direction of the applied force, a=F/m
a-acceleration, f-force, m-mass. (This is Newton's
second law)
- Force is the interaction
of 2 objects£∫the acting and reacting forces
between the two interacting objects are always equal
in magnitude and opposite in direction, acting on
the same straight line. (This is Newton's third
law)
There are also some basic
concepts:
- Force: The action of one
object on another object, the result of which can
produce acceleration or deformation, the unit of
force is N (Newton).
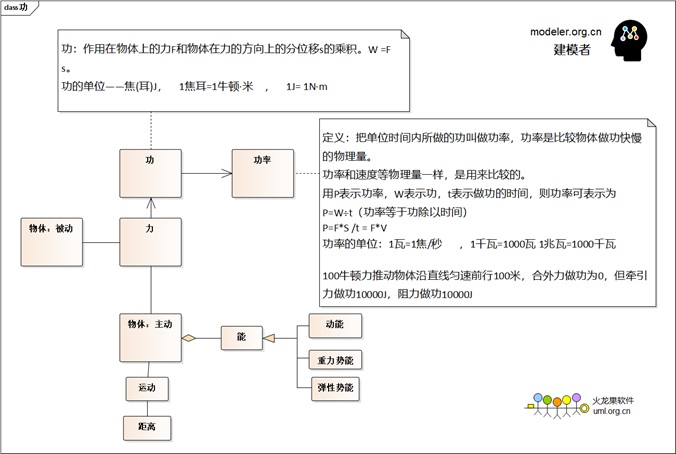
- Work: An object A exerts a
force F on another object B, causing this object
to move some distance in the direction of the force,
that is, say Object A does work on object B. It
can also be said that the force F does work on object
B. The product of the force F acting on the object
and the displacement s s of the object in the direction
of the force is the quantity of work. W =F s°£ The
unit of work - joule (ear) J, 1 joule = 1 Newton
°§ m , 1J = 1N °§ m
- Energy (energy): If an object
can do work externally, it needs to have energy,
referred to as energy.
The basic properties of the force
are also broken down:
- The three elements of force:
the point of application, the direction, and the
magnitude
- 2. Force balance: After the
object is subjected to the action of 2 forces, it
still maintains the original state of inertia (stationary
or uniform linear motion state)
These are modeled as follows:
Diagrams are helpful for analysis,
but the order of reading is more arbitrary, and words
are conducive to arranging the order of reading, so
the meaning expressed in the above diagram is described
in words as follows, in natural language, the most
important thing is nouns and verbs, which express
objects and actions respectively. In order to distinguish
between nouns and verbs, in the following textual
descriptions, the nouns are in Chinese and the verbs
are in English.
- objects have motion,
- Motion has velocity, and
velocity has inertia
- The change in the velocity
of an object is called acceleration (called).
- The force of the subject
on the object can be generated
- The process by which the
body exerts force can do work
- The main body that can do
work has energy
- Force has three elements:
the point of application, the direction, and the
magnitude
- Multiple forces can be synthesis,
- If two forces are equal in
magnitude and opposite in direction, the name (called)
is the equilibrium of the two forces
For each force, there is a model
framework, which is described in class diagrams for
analysis, and table descriptions are easy to write
and read, so the key content in each diagram is listed
"Force Analysis Table":
| Various
forces |
Object-action
relations |
The
Three Elements of Force (Properties of Force) |
Application
scenarios |
| Point
of effect/surface |
Direction |
Size
calculation method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following is an analysis of
each force according to the model framework of the
force: elastic force, gravity, friction force, pressure,
buoyancy
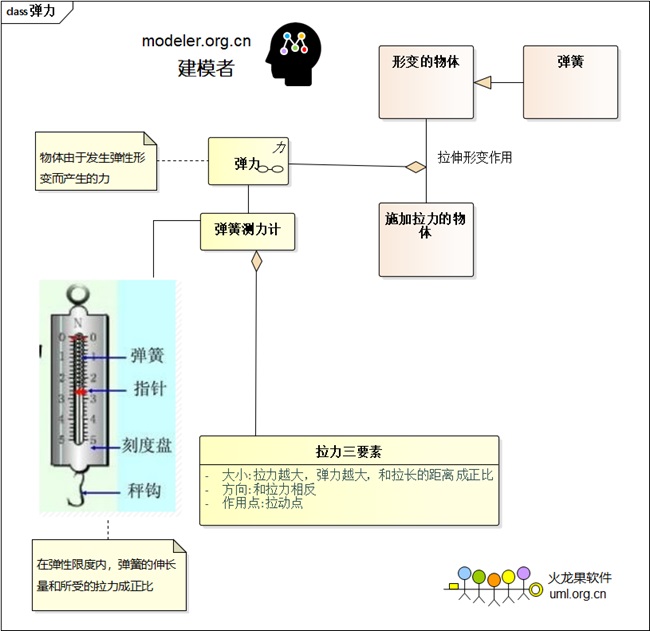
Elastic Modeling:
Force Analysis Table:
| Various
forces |
Object-action
relations |
The
Three Elements of Force (Properties of Force) |
Application
scenarios |
| Point
of effect/surface |
Direction |
Size
calculation method |
| 1. Elasticity |
One object pulls or squeezes another
object to produce deformation, and the deformed
object reacts |
2 object contact points/surfaces |
Reversal of the deformation trend |
According to the proportional relationship
between the distance of the deformation and the
magnitude of the force |
Spring tension gauge |
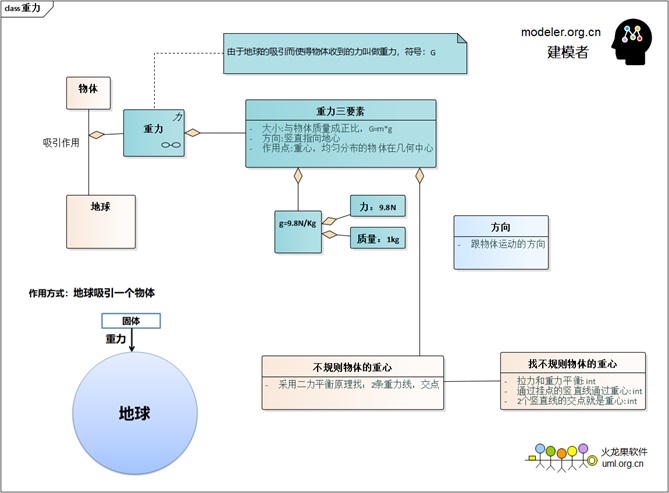
Gravity Modeling:
Force Analysis Table:
| Various
forces |
Object-action
relations |
The
Three Elements of Force (Properties of Force)£© |
Application
scenarios |
| Point
of effect/surface |
Direction |
Size
calculation method |
| 2. Gravity |
The attraction of the earth to an object |
Barycenter |
Straight down |
G=mg |
The
scale apples fall to the ground
|
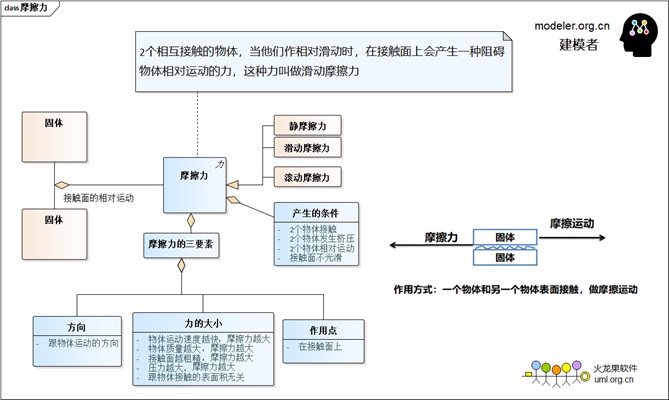
Friction Modeling:
Force Analysis Table:
| Various
forces |
Object-action
relations |
The
Three Elements of Force (Properties of Force) |
Application
scenarios |
| Point
of effect/surface |
Direction |
Size
calculation method |
| 3. Frictional force |
The effect of frictional motion on the contact
surfaces of two objects |
Friction surfaces |
Reverse of frictional motion |
Reverse of frictional motion |
Non-slip road
brakes |
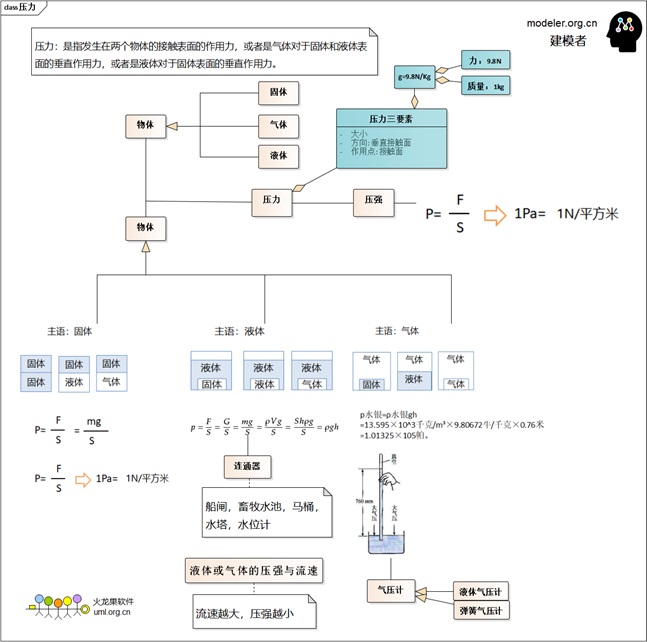
Pressure frame mold construction:
Force Analysis Table:
| Various
forces |
Object-action
relations |
The
Three Elements of Force (Properties of Force) |
Application
scenarios |
| Point
of effect/surface |
Direction |
Size
calculation method |
| 4. Pressure |
The effect of one object squeezing another |
Contact surfaces |
And the contact surface perpendicular |
There are three calculation methods: solid,
liquid, and gas |
Submarine
rollers |
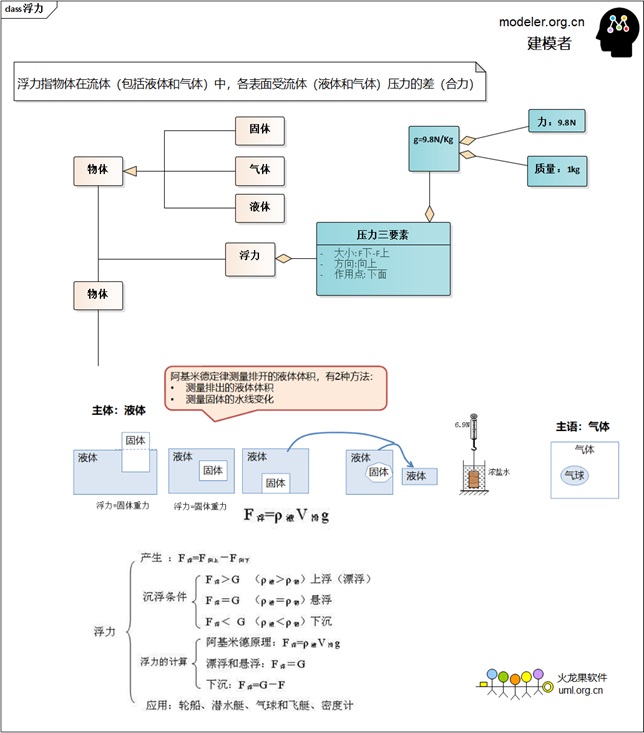
Buoyancy Modeling:
Force Analysis Table:
| Various
forces |
Object-action
relations |
The
Three Elements of Force (Properties of Force) |
Application
scenarios |
| Point
of effect/surface |
Direction |
Size
calculation method |
| 5. Buoyancy |
An object floats in/on a liquid or gas |
Ground |
Vertically up |
Pressure below - pressure above |
The balloon is in the air and the
boat is on the water |
Modeling of work, power, and
mechanical energy:
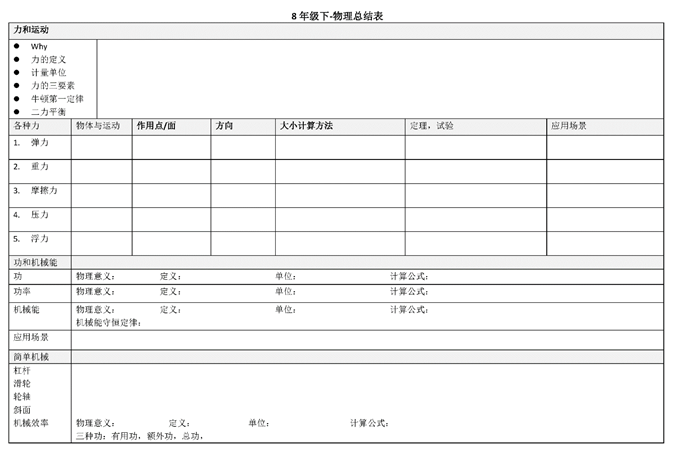
Representation of knowledge after
domain modeling:
These are some of the knowledge
that takes force as the research perspective in the
laws of mechanical motion. These models should be
very useful for understanding knowledge, but for students,
it is undoubtedly still complicated, and the description
of book knowledge needs to be applied to students
after clear logical relationships.
Postscript
I hope you have benefited from reading this.
If you are willing to share your experience, please submit it to us.
If you are interested in our training, consulting and tools:
| 